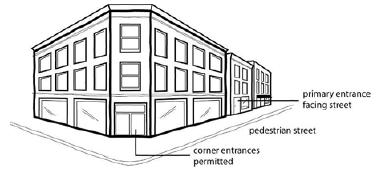
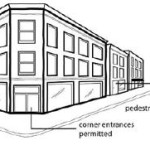
The stretch of Ludlow Avenue from Whitfield Avenue to the west to Ormond Avenue to the east has a decidedly suburban form different from the rest of the gaslight district between Ormond Avenue and Clifton Avenue. This western stretch is part of a two-block commercial main street that is arguably the “most complete neighborhood commercial district in the city,” according to Aaron Renn.
Just being a commercial main street, however, has not been enough to preserve the pedestrian-oriented nature of the street for the entire western half of the district on the south side of Ludlow, and a key gap on the north side of Ludlow at Ormond.
The southern stretch could be described as the Clifton financial district. Between Whitfield and the CVS are three banks – US Bank, PNC and Columbia Savings Bank – all with their own independent access and parking lots surrounding the buildings.
The oddity is not that banks have their own access and parking, but that you have auto-oriented suburban development on a historic commercial main street. This is not a unique problem, but a pedestrian streets ordinance, perhaps modeled after Chicago’s, could help correct faulty land use decisions like this one.
The theory behind such an ordinance is that you have an A and B street hierarchy, with A streets having a high standard of spatial definition and pedestrian interest in a continuous network, and B streets having lower standards for parking lots, drive-thru’s, muffler shops, etc.
This is a neoliberal approach typical of New Urbanism, It compromises for many areas and gives businesses a design choice based on location: a pedestrian main street (A), or an auto-oriented B street.
Chicago’s pedestrian streets ordinance seeks “to preserve and enhance the character of streets and intersections that are widely recognized as Chicago’s best examples of pedestrian-oriented shopping districts. The regulations are intended to promote transit, economic vitality and pedestrian safety and comfort.”
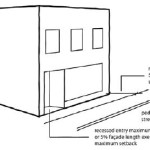
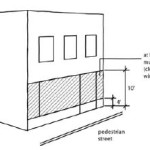
The ordinance then sets the criteria for the pedestrian street designation, lists all street segments within the city that have been deemed pedestrian streets subject to the ordinance, and sets standards for build-to lines, transparency and pedestrian access.
Of particular importance is what it says about parking and driveways:
Parking Location. All off-street parking spaces must be enclosed or located to the rear of the principal building and not be visible from the right-of-way of a pedestrian street.
Driveways and Vehicle Access. Vehicle access to lots located along pedestrian streets must come from an alley. No curb cuts or driveways are allowed from a pedestrian street.
If this the stretch of Ludlow Avenue had a pedestrian streets ordinance, at such time these banks wish to make improvements or redevelopment, these standards would then kick in and require the banks to reconsider their vehicular access, possibly to the point of eliminating driveways and consolidating parking and access off Whitfield.
More realistically, however, the ordinance would help guard other commercial main streets from the auto-oriented nature of drug stores, banks and restaurants without the need for a short-term Interim Development Controls (IDC) district or historic district protections.